ANDROID TECHNOLOGY
Android Technology
What is Android?
Android is an open source and Linux-based Operating System
for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers.
Different version of Android system
Android version 1.0 – Astro
Android version 1.1 – Beta
Android version 1.5 – cupcake
Android version 1.6 – donut
Android version 2.0 – Eclaire
Android version 2.2 – FRO YO
Android version 2.3 – Ginger-Bread
Android version 3.0, 3.1,3.2- Honeycomb
Android version 4.0 – Ice cream sandwich
Android version 4.2 – jellybean
Android version 4.4 - kitkat
Android version 5.0,5.1 – lollipop
Android version 6.0 – marshmallow
Android version 7.0 – Nougat
History of Android:-
Android was developed by the Open Handset Alliance, led by
Google, and other companies. The first beta version of the Android Software
Development Kit (SDK) was released by Google in 2007 where as the first
commercial version, Android 1.0, was released in September 2008.
On June 27, 2012, at the Google I/O conference, Google announced
the next Android version, 4.1 Jelly Bean. Jelly Bean is an incremental update,
with the primary aim of improving the user interface, both in terms of
functionality and performance.
Features of Android:-
Android is a powerful operating system competing with Apple
4GS and supports great features. Few of them are listed below:
Feature
|
Description
|
Beautiful UI
|
Android OS
basic screen provides a beautiful and intuitive user interface.
|
Connectivity
|
GSM/EDGE,
IDEN, CDMA, EV-DO, UMTS, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, LTE, NFC and WiMAX.
|
Storage
|
SQLite, a
lightweight relational database, is used for data storage purposes.
|
Media
support
|
H.263,
H.264, MPEG-4 SP, AMR, AMR-WB, AAC, HE-AAC, AAC 5.1, MP3, MIDI, Ogg Vorbis,
WAV, JPEG, PNG, GIF, and BMP
|
Messaging
|
SMS and MMS
|
Web browser
|
Based on the
open-source WebKit layout engine, coupled with Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine
supporting HTML5 and CSS3.
|
Multi-touch
|
Android has
native support for multi-touch which was initially made available in handsets
such as the HTC Hero
|
Multi-tasking
|
User can
jump from one task to another and same time various application can run
simultaneously
|
Resizable
widgets
|
Widgets are
resizable, so users can expand them to show more content or shrink them to
save space
|
Multi-Language
|
Supports single
direction and bi-directional text.
|
GCM
|
Google Cloud
Messaging (GCM) is a service that lets developers send short message data to
their users on Android devices, without needing a proprietary sync solution.
|
Wi-Fi Direct
|
A technology
that lets apps discover and pair directly, over a high-bandwidth peer-to-peer
connection
|
Android Beam
|
A popular
NFC-based technology that lets users instantly share, just by touching two
NFC- enabled phones together.
|
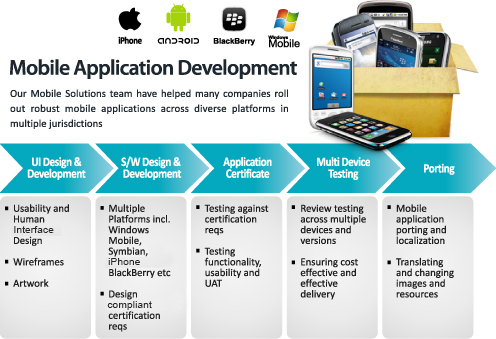
Android Applications
Android applications are usually developed in the Java
language using the Android Software Development Kit.
Once developed, Android applications can be packaged easily
and sold out either through a store such as Google Play or the Amazon Appstore.
Android powers hundreds of millions of mobile devices in more
than 190 countries around the world. It's the largest installed base of any
mobile platform and growing fast. Every day more than 1 million new Android
devices are activated worldwide.
This tutorial has been written with an aim to teach you how
to develop and package Android application. We will start from environment
setup for Android application programming and then drill down to look into
various aspects of Android applications.





Comments
Post a Comment